Colours
Distinguishing features
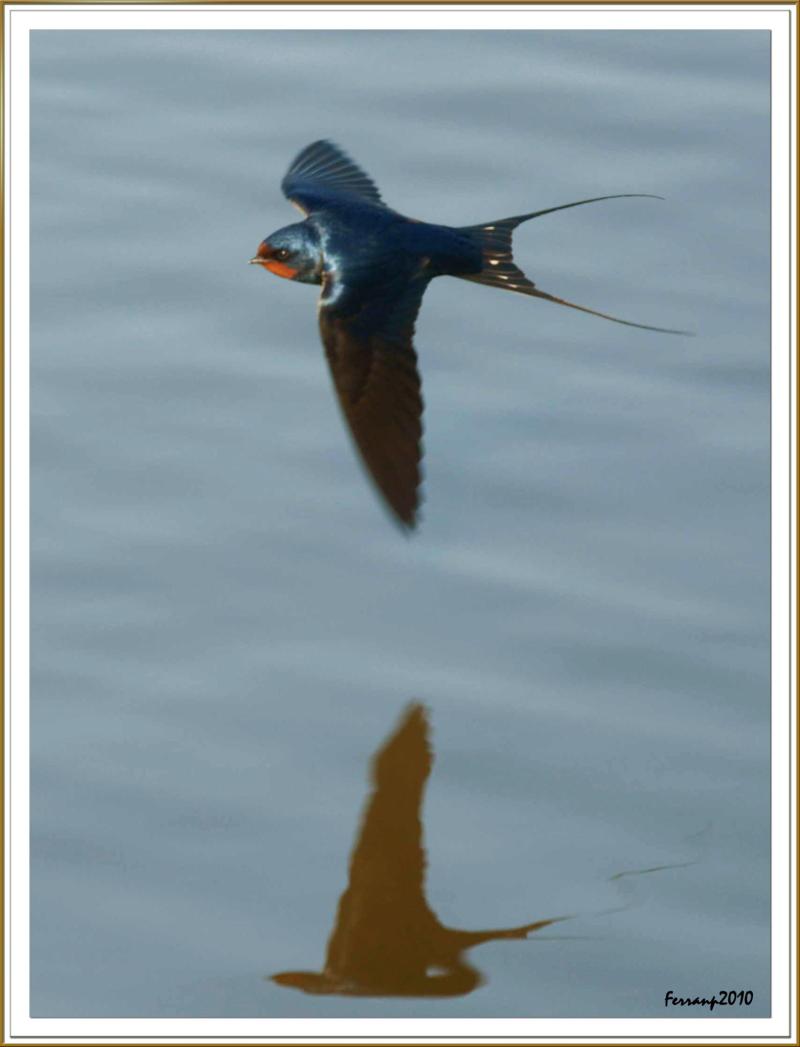
It has steel blue upperparts and a rufous forehead, chin and throat, which are separated from the off-white underparts by a broad dark blue breast band. The outer tail feathers are elongated, giving the distinctive deeply forked swallow tail. There is a line of white spots across the outer end of the upper tail.
The female is similar in appearance to the male, but the tail streamers are shorter, the blue of the upperparts and breast band is less glossy, and the underparts more pale. The juvenile is browner and has a paler rufous face and whiter underparts. It also lacks the long tail streamers of the adult.
The distinctive combination of a red face and blue breast band render the adult Barn Swallow easy to distinguish from the African Hirundo species and from the Welcome Swallow (Hirundo neoxena) with which its range overlaps in Australasia. (Wikipedia)
Size
- From 17 cm to 19 cm (Includes the 27cm elongated tail feathers)
Wingspan
- From 32 cm to 34.5 cm
Synonyms
Distribution
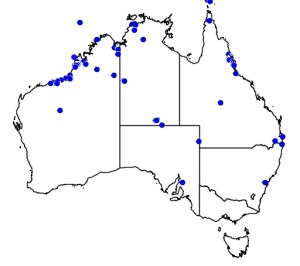
Distribution and habitat preferences
The preferred habitat of the Barn Swallow is open country with low vegetation, such as pasture, meadows and farmland, preferably with nearby water. This swallow avoids heavily wooded or precipitous areas and densely built-up locations. The presence of accessible open structures such as barns, stables, or culverts to provide nesting sites, and exposed locations such as wires, roof ridges or bare branches for perching, are also important in the bird's selection of its breeding range. (Wikipedia)
Diet
It typically feeds 7–8 metres above shallow water or the ground, often following animals, humans or farm machinery to catch disturbed insects, but it will occasionally pick prey items from the water surface, walls and plants.
In breeding areas, large flies make up around 70% of the diet, with aphids are also a significant dietary component.
On wintering grounds, Hymenoptera, especially flying ants, are important food items. (Wikipedia)