Colours
Distinguishing features
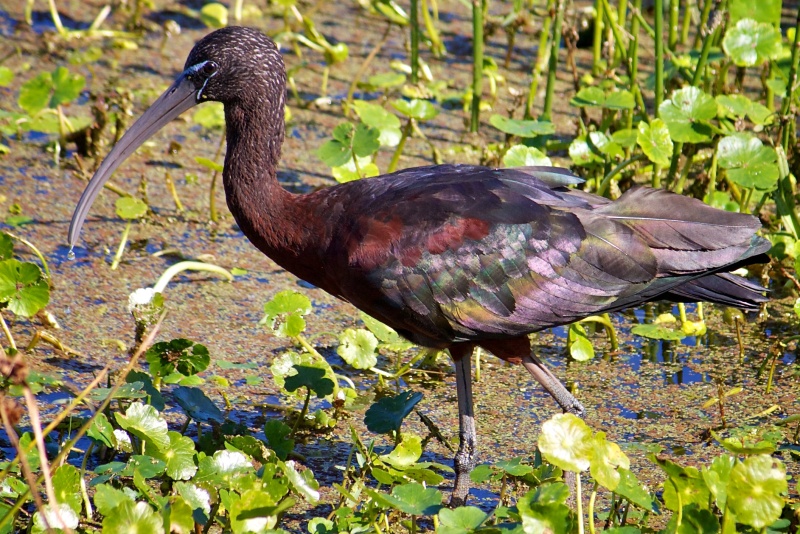
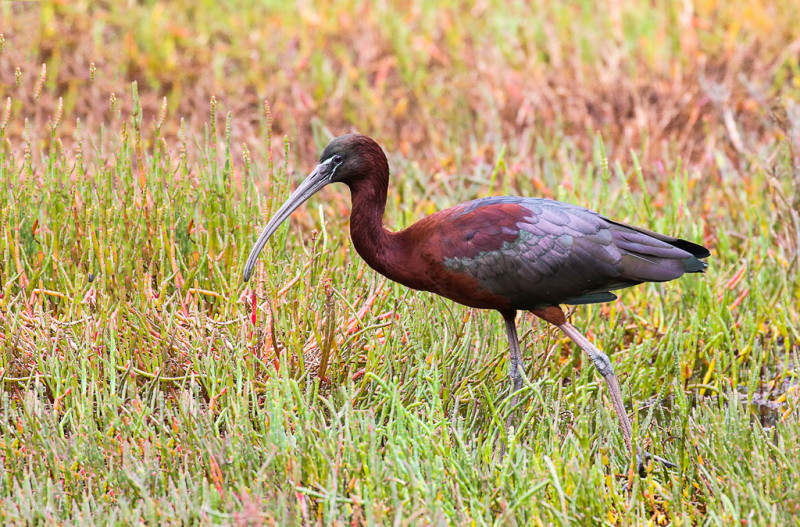
Breeding adults have reddish-brown bodies and shiny bottle-green wings. Non-breeders and juveniles have duller bodies. This species has a brownish bill, dark facial skin bordered above and below in blue-gray (non-breeding) to cobalt blue (breeding), and red-brown legs. (Wikipedia)
Size
- From 55 cm to 65 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- From 88 cm to 105 cm
Synonyms
Similar taxa
-
Animalia:
White-faced Ibis (species: Plegadis chihi)
Plegadis chihi is very similar to Plegadis falcinellus in its non-breeding plumages, but it tends to be slightly smaller and the plumage color is somewhat warmer. Breeding adults have a pink bare face bordered with white feathers (rather than a bluish bare face with no bordering feathers), a grey bill, and brighter colored, redder legs. Adults have red eyes year-round, whereas Plegadis falcinellus have dark eyes. Juveniles of the two species are nearly identical. (Wikipedia)
Distribution
Distribution and habitat preferences
This is the most widespread ibis species, breeding in scattered sites in warm regions of Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Atlantic and Caribbean region of the Americas.
They feed in very shallow water and nest in freshwater or brackish wetlands with tall dense stands of emergent vegetation such as reeds, papyrus or rushes) and low trees or bushes. They show a preference for marshes at the margins of lakes and rivers but can also be found at lagoons, flood-plains, wet meadows, swamps, reservoirs, sewage ponds, paddies and irrigated farmland. It is less commonly found in coastal locations such as estuaries, deltas, salt marshes and coastal lagoons. Preferred roosting sites are normally in large trees which may distant from the feeding areas. (Wikipedia)
Diet
Prey includes adult and larval insects such as aquatic beetles, dragonflies, damselflies, grasshoppers, crickets, flies and caddisflies, Annelida including leeches, molluscs (e.g. snails and mussels), crustaceans (e.g. crabs and crayfish) and occasionally fish, amphibians, lizards, small snakes and nestling birds. (Wikipedia)