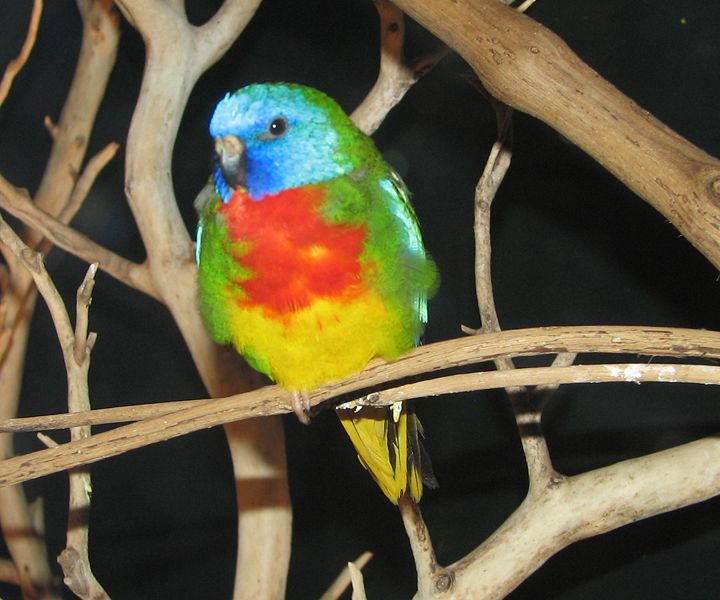
©NSW Government, Australia: Scarlet-chested Parrot (Neophema (Neophema) splendida) male on the right and female on the left
Colours
Distinguishing features
This small vibrant and brightly coloured parrot is sexually dimorphic. The male has a scarlet chest, a cobalt blue face, and bright green upperparts. The lower breast and underparts are yellow, and the wing coverts are pale blue. The tail is green, the eyes are brown and the bill is blackish, and legs are brown-grey.
The female likewise has a blue face, although the coloration is less extensive, green upperparts and green breast, with yellow underparts.
Immature birds are duller versions of their respective adult forms. Males begin to get red plumage on their chest from around two or three months of age, though do not complete their red chest until fifteen to eighteen months old. (Wikipedia)
Size
- From 19 cm to 21 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- Up to 40 cm
Synonyms
Similar taxa
-
Animalia:
Turquoise Parrot (species: Neophema (Neophema) pulchella)
The female Scarlet-chested Parrot resembles the female Turquoise Parrot of eastern Australia, but can be distinguished by the blue lores and paler blue wing patch. (Wikipedia)
Distribution
Distribution and habitat preferences
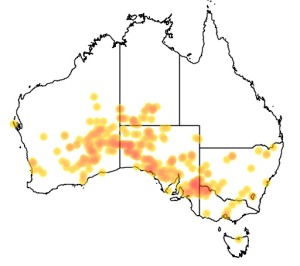
The Scarlet-chested Parrot is sparsely scattered across the dryer southern parts of the Australian continent, from Pingelly, Corrigin and Laverton in Western Australia east across South Australia and into the southern Northern Territory and into far western New South Wales. They inhabit dry Eucalyptus and Acacia scrubland and grassland, including Atriplex and Triodia. (Wikipedia)
Diet
Seeds of grasses make up the diet, and they are thought to utilise succulent plants such as Calandrinia to meet much of their fluid requirement. (Wikipedia)