Colours
Distinguishing features
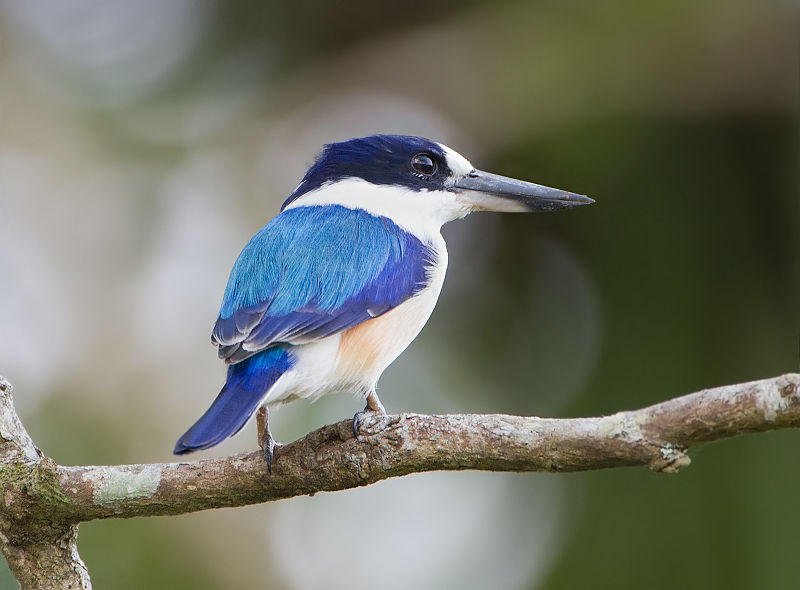
It has blue wings, head and tail with white breast, abdomen and nape. It has a white patch in front of the eyes and a black band stretching from the bill, through the eyes and to the ear coverts. A white patch is visible on the wings in flight. The female is distinguished by a blue rather than white nape. The iris is dark brown and the legs and feet dark grey. Immature birds are duller with a blackish crown. (Wikipedia)
Size
- Up to 25.5 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- Wingspan data is not yet available.
Synonyms
Distribution
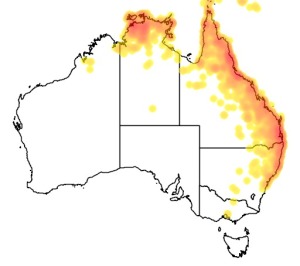
Distribution and habitat preferences
It is native to Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Australia, where it is found on or near the Australian Coastline from Port Stephens in New South Wales northwards to Cape York and westwards across the Top End. It is a summer visitor in the southern parts of its range in New South Wales and southern Queensland; elsewhere it is resident all year round.
As its name suggests, it inhabits subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, and subtropical or tropical mangrove forests and Melaleuca swampland. (Wikipedia)
Audio recordings
Recorded at Kakadu National Park (near Kakadu), Northern Territory in Australia
© Marc Anderson
(source)
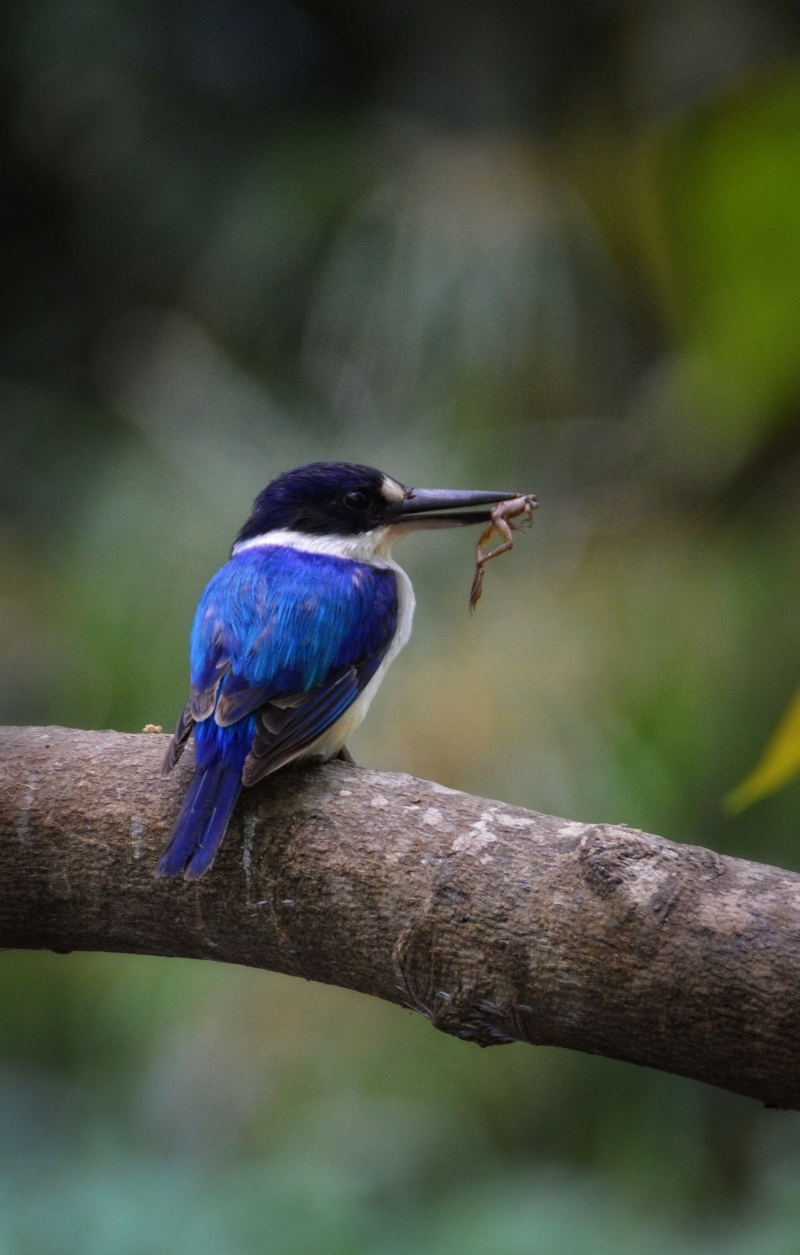
Diet
It hunts invertebrates, such as bugs, beetles, grasshoppers, spiders, and worms, as well as small frogs and lizards. It often kills prey by hitting it against a branch after seizing it. (Wikipedia)