Colours
Distinguishing features
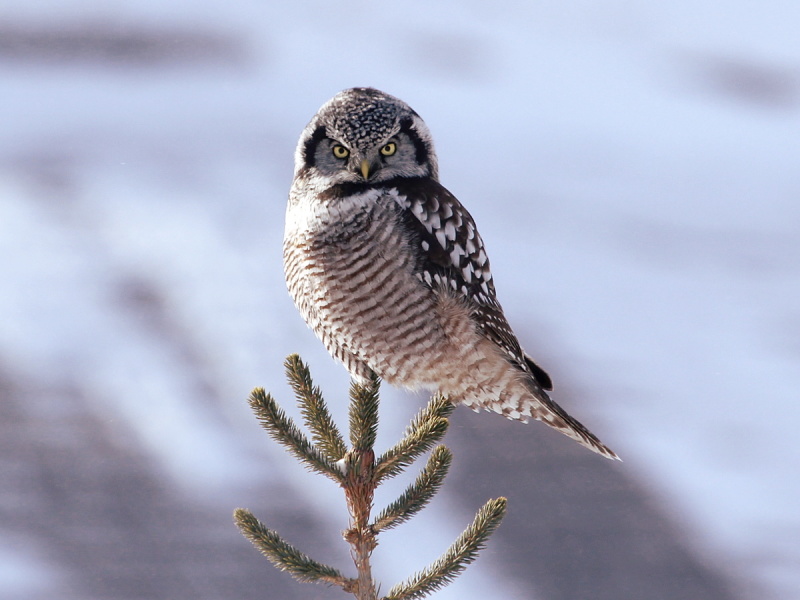
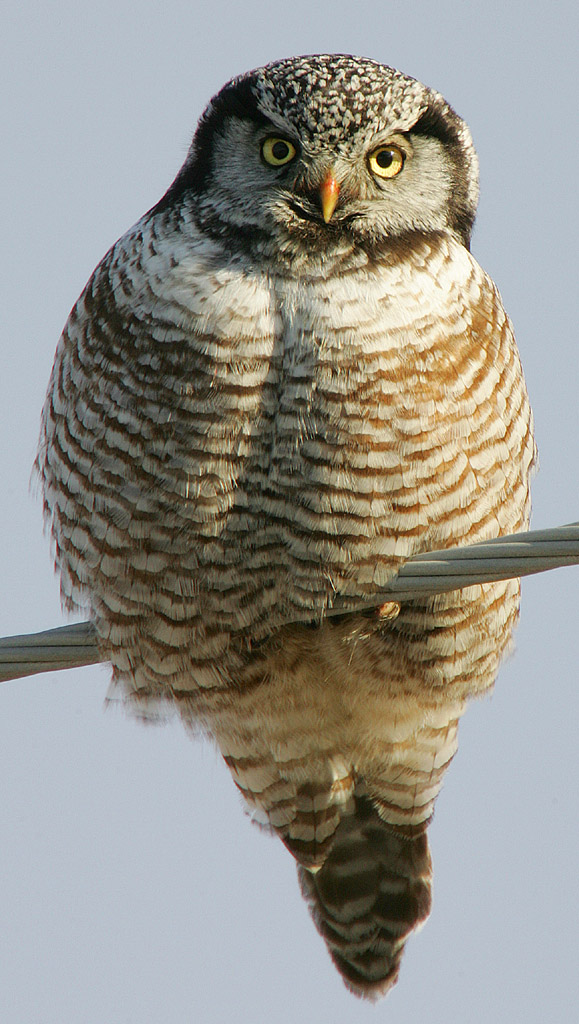
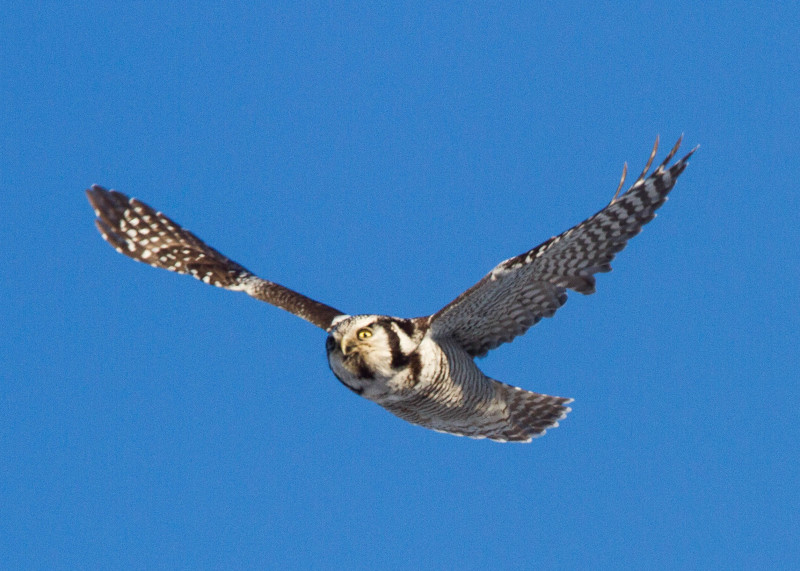
Its plumage is relatively dark brown with an off white spotting pattern on all dorsal parts of the body with the exception of the back of the neck which boasts a black v-shaped pattern. The underbelly is generally white or off-white which continues to the toes with brown bands on the breast and stomach. It also has a long tail with brown banding. It has a smokey white face with a black border, a flat head, yellow eyes and a yellow curved beak. (Wikipedia)
Size
- Up to 45 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- Up to 89 cm
Synonyms
Distribution
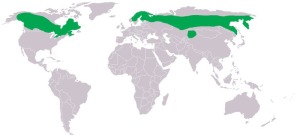
Distribution and habitat preferences
The North American subspecies S.u.caparoch spans from eastern Alaska through to Newfoundland and in some areas extends south into northern United States. The other two subspecies are found in Eurasia: S. u. tianschanica breeds in central Asia reaching Xinjiang (China) and S. u. ulula resides across Eurasia reaching Siberia at its most eastern range.
Occasionally, S.u.caparoch can extend its territory as far south as northern Minnesota and many other states in the northern United States including more central states such as West Virginia, New York, and South Dakota. These southern forays into the northern United States are rare and generally occur during winter, or following an explosion in a population of prey.
They are unevenly distributed and highly variable throughout the boreal forest. They live mostly in open coniferous forests, or coniferous forests mixed with deciduous species such as larch, birch, poplar, and willow. They are found in muskegs, clearings, swamp valleys, meadows, or recently burnt areas, and generally avoid dense spruce-fir forests.(Wikipedia)
Diet
It feeds on a variety of prey, which can include small rodents to mammals more robust in size, and a variety of birds. (Wikipedia)