Colours
Distinguishing features
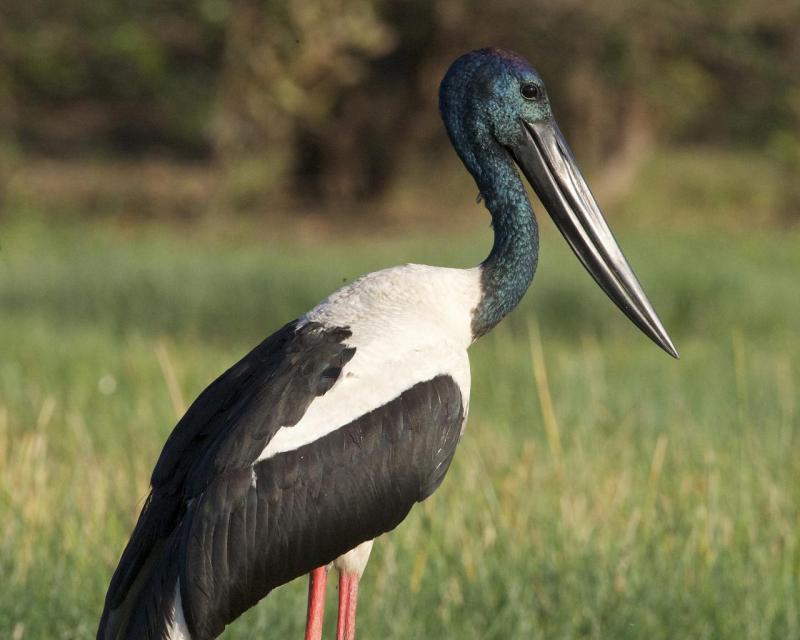
The plumage patterns are conspicuous with younger birds differing from adults. Adults have a glossy bluish-black iridescent head, neck, secondary flight feathers and tail; a coppery-brown crown; a bright white back and belly; bill black with a slightly concave upper edge; and bright red legs. The sexes are identical but the adult female has a yellow iris while the adult male has it brown. Juveniles younger than 6 months have a brownish iris; a distinctly smaller and straighter beak; a fluffy appearance; brown head, neck, upper back, wings and tail; a white belly; and dark legs. Juveniles older than 6 months have a mottled appearance especially on the head and neck where the iridescence is partly developed; dark-brown outer primaries; white inner primaries that forms a shoulder patch when the wings are closed; a heavy beak identical in size to adults but still straighter; and dark to pale-pink legs.
Like most storks, it flies with the neck outstretched, not retracted like a heron. In flight it appears spindly and a black bar running through the white wings with black neck and tail make it distinctive. (Wikipedia)
Size
- From 112 cm to 115 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- Up to 200 cm
Synonyms
Comments
The Jabirus only visit Buladelah occasionally but we are always excited when they arrive.
by Geoffrey Shuetrim
Distribution
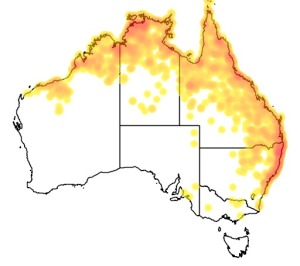
Distribution and habitat preferences
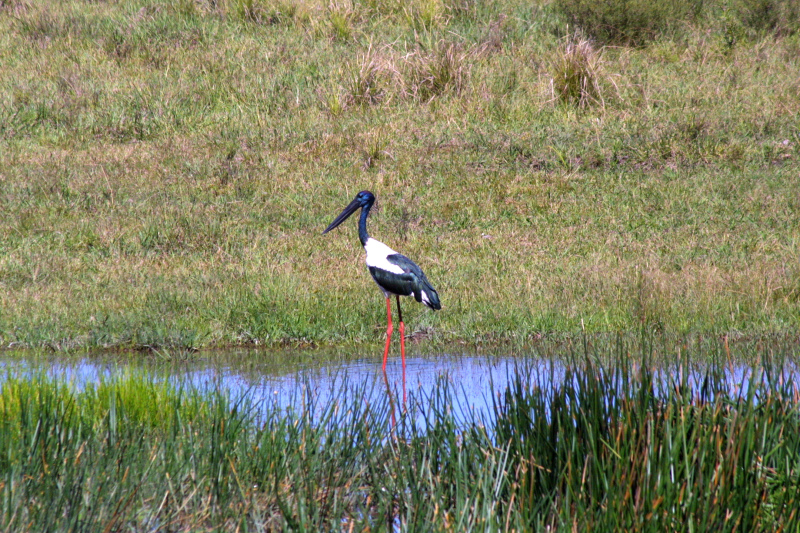
It is a resident species across South and Southeast Asia with a disjunct population in Australia. It lives in wetland habitats to forage for a wide range of animal prey. (Wikipedia)
Behaviour
Very shy - need to take photos with a good telephoto lens. Alternatively you can drive by in a vehicle and they do not recognise this as a human.
Diet
Their diet includes fish, crabs, molluscs, insects (grasshoppers and beetles), amphibians, reptiles and quite large birds.