Colours
Distinguishing features
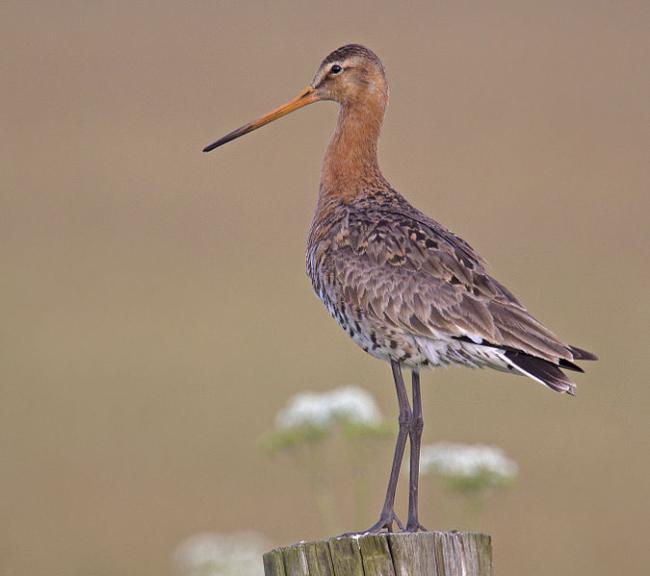
It has a long bill (7.5 cm to 12 cm long), neck and legs. During the breeding season, the bill has a yellowish or orange-pink base and dark tip; the base is pink in winter. The legs are dark grey, brown or black. The sexes are similar, but in breeding plumage, they can be separated by the male's brighter, more extensive orange breast, neck and head.
In winter, adults have a uniform brown-grey breast and upperparts (in contrast to the Bar-tailed Godwit's streaked back).
Juveniles have a pale orange wash to the neck and breast.
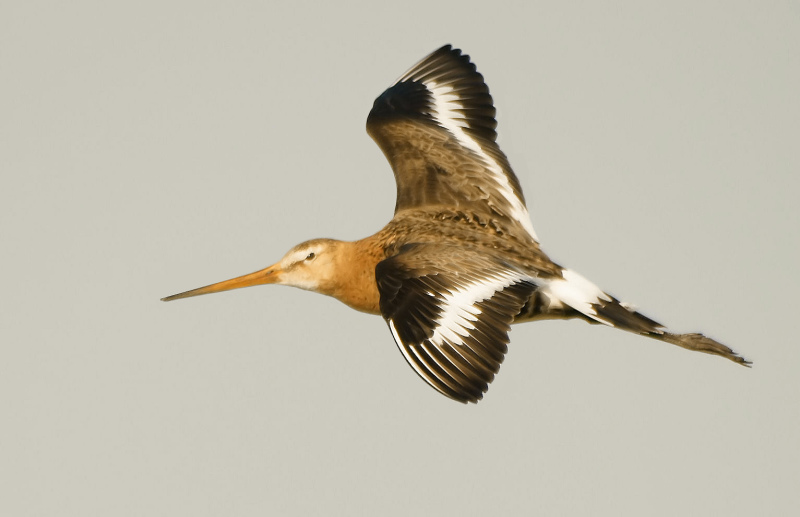
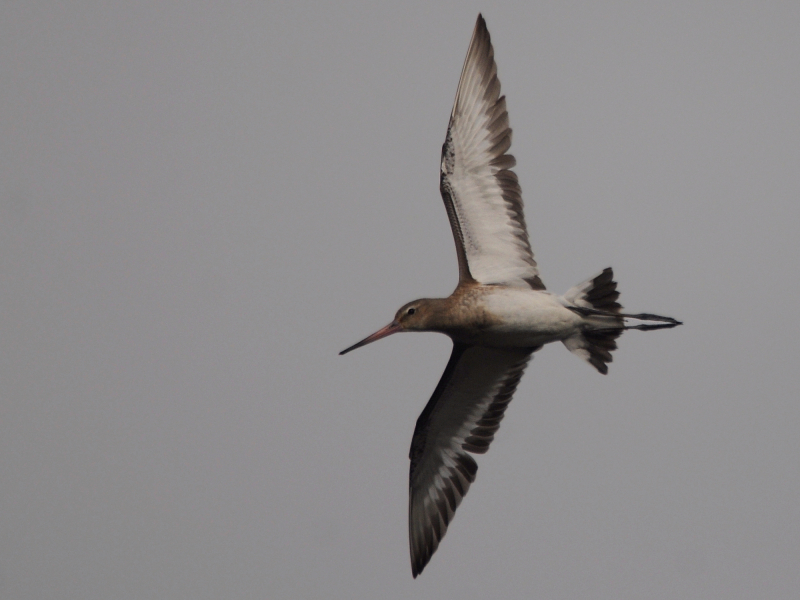
In flight, its bold black and white wingbar and white rump can be seen readily. (Wikipedia)
Size
- From 36 cm to 43 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- From 70 cm to 82 cm
Synonyms
Similar taxa
-
Animalia:
Bar-tailed Godwit (species: Limosa lapponica)
Limosa lapponica is stockier-looking when flying, with shorter legs that barely extend beyond its tail. The Limosa lapponica plumage resembles a Curlew or a Whimbrel, being essentially brown with a barred tail; most significantly, it lacks a wing-bar and shows a white 'V' up its back. When on the ground the Limosa limosa can be difficult to separate from the similar Limosa lapponica, but the Limosa limosa has a longer, straighter bill and longer legs, which are diagnostic. Limosa limosa are similar in body size and shape to Limosa lapponica, but stand taller.
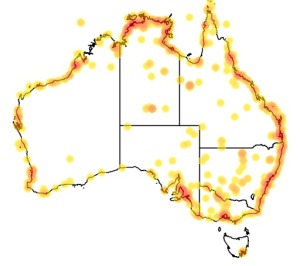
Distribution
Distribution and habitat preferences
Its breeding range stretches from Iceland through Europe and areas of central Asia. They spend winter in areas as diverse as the Indian Subcontinent, Australia, western Europe and west Africa. The species breeds in fens, lake edges, damp meadows, moorlands and bogs and uses estuaries, swamps and floods in winter. (Wikipedia)
Diet
They mainly eat invertebrates, but also aquatic plants in winter and on migration. In the breeding season, prey includes include beetles, flies, grasshoppers, dragonflies, mayflies, caterpillars, annelid worms and molluscs. Occasionally, fish eggs, frogspawn and tadpoles are eaten. In water, the most common feeding method is to probe vigorously, up to 36 times per minute, and often with the head completed submerged. On land, they probe into soft ground and also pick prey items from the surface. (Wikipedia)
Web resources
References
- Simpson, K., N. Day and P. Trusler (2004). Field Guide to Birds of Australia: 7th Edition Penguin Group (Australia), Camberwell, Victoria.