Colours
Distinguishing features
It is generally a black bird with white in the wing, undertail coverts, the base of the tail and most visibly, the tip of the tail. It has yellow eyes.
The wings are long and broad. The long and heavy bill is about one and a half times as long as the head and is hooked at the end. Juvenile birds have similar markings to adults but have softer and brownish plumage overall, although the white band on the tail is narrower. The upperparts are darker brown with scallops and streaks over the head and neck, and the underparts lighter brown. The eyes are dark brown and the bill dark with a yellow tip. The gape is a prominent yellow.
Older birds grow darker until adult plumage is achieved, but juvenile tail markings only change to adult late in development. (Wikipedia)
Size
- From 41 cm to 51 cm (Length of specimen)
Wingspan
- From 56 cm to 77 cm
Synonyms
Distribution
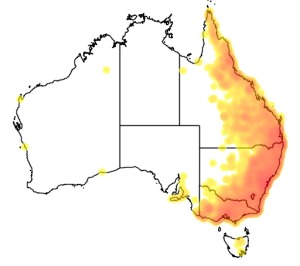
Distribution and habitat preferences
It is common in both wet and dry sclerophyll forests, rural and semi-urban environments throughout eastern Australia, from Cape York Peninsula to western Victoria and Lord Howe Island, where it occurs as an endemic subspecies. In general, it is sedentary, although some populations from higher altitudes move to areas of lower elevation in winter. (Wikipedia)
Diet
It is an omnivorous and opportunistic feeder, eating fruit and berries as well as preying on many invertebrates, and smaller vertebrates, mostly juvenile birds and bird eggs.
They will hunt in trees, snatching birds and eggs from nests, as well as insects and berries from trees. They also hunt in the air and on the ground. Insects predominate in the diet during summer months, and fruit during the winter. They will often scavenge, eating scraps and rubbish and can be quite bold when seeking food from people, lingering around picnic areas and bird-feeding trays.
Beetles and ants are the most common types of insects consumed. They have been recorded taking mice, as well as chickens and turkeys from farms.They also consume fruit, including a wide variety of figs, such as the Moreton Bay (Ficus macrophylla), Port Jackson (F. rubiginosa), Banyan (F. virens) and Strangler fig (F. watkinsiana),[43] as well as lillypillies (Syzygium species), white cedar (Melia azedarach), plum pine (Podocarpus elatus), and geebungs (Persoonia species). Other fruit is also sought after, and they have been known to raid orchards, eating apples, pears, strawberries, grapes, stone fruit, citrus, and corn. (Wikipedia)